So Active Directory can do some cool things around distinguishedNames (DNs) that many developers even this long into the availability of the product don’t know or take advantage of. I mention this because yet again I ran into a case where some developer/application integrator was unhappy about how easy it is to move users around in the hierarchy of Active Directory because it made it difficult to bind to the userid…
Now I expect most AD Admins probably don’t think twice about this but anyone who has come from other LDAP directory platforms have a more “that DN better not EVER change” attitude… Why? Because for their bind IDs they need to know the exact DN or else they can’t bind. Trouble that eh?
Bind Formats
So the first thing we will discuss is the “DN” formats available for binding. AD only offers one format that could honestly be called a DN format, but since the term most often used in applications and in general discussion is Bind DN I will stick with the “DN Format” label.
Format 1:
An actual real live DN in the normal DN format like CN=joe,OU=Users,OU=My,DC=test,DC=loc. Canonically that looks like test.loc/My/Users/joe. For those who like pretty pics it is this user…
With AdFind you could specify this bind DN like so
adfind -default -f name=joe -u cn=joe,ou=users,ou=my,dc=test,dc=loc -up SomePassword123!
Various other programs would have other methods of specifying it, if you use those programs, you should be able to work out the method.
This is the most used/widespread bind DN format for directories and hence applications. For Active Directory it is pretty much your worse choice because it is the most susceptible to breaking. I don’t like to be too direct with things like this but if you don’t know what you are doing, just don’t use this format. It will save you issues later.
Format 2:
This is a very familiar format to Windows users and admins as they have lived with it for 15 or more years… However, anyone from some other directory environment will probably look at you in disgust if you mention it… The format is Domain\UserId; this is the standard Windows NT format. So for the previous example the ID would be test\joe. Not only is that shorter, but it has no dependence on the location in the directory where the userID is located, at least within the domain. I could move “joe” to the Domain Controllers OU (not that I normally would) and no programs nor scripts nor tools nor anything else using that Bind DN format would need to be changed.
With AdFind you could specify this bind DN like so
adfind -default -f name=joe -u test\joe -up SomePassword123!
Note: If you have but a single domain, it is also safe to omit the [domain\] from the bind DN.
Format 3:
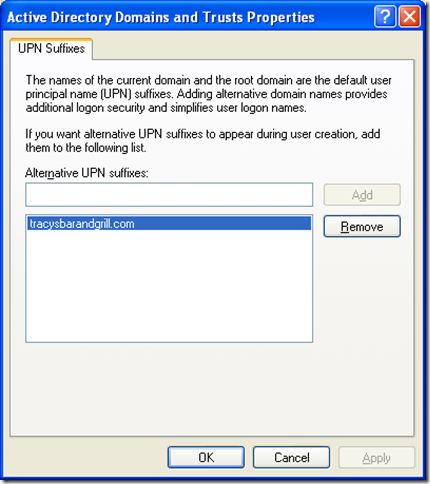
This is newer format that neither the old Windows folks nor the old other platform directory folks likely are familiar with. We call it the UPN format because it utilizes the userPrincipalName attribute of the userid. Now this attribute may or may not be populated but whether it is or not, all user’s have a UPN. If nothing specific is specified for a userid, the UPN is their sAMAccountName followed by an @ symbol followed by the domain in dot format. So for the previous example… joe@test.loc. One nice thing about this format is that it *should* work uniquely across an entire forest. So if you move a user even between domains it could be configured to still be fine. But joe… you said it had the domain in the attribute, wouldn’t that change? Well yes reader, if you stick with the default if I move my userid joe from test.loc to child.test.loc then my default UPN will then become joe@child.test.loc but you don’t have to leave the default, you can set what you want… For instance I could set my UPN to actually just be joe@test.loc and regardless of the domain moved to it would stay that way. I could even set it to joe@tracysbarandgrill.com if I wanted to. Of course if you set that value you should also set the allowed (or alternate) UPN Suffixes in the forest to allow for it. That way people can set that suffix in ADUC and so other things with forest trusts all work properly. Strictly speaking for use within a single forest though you don’t need it. You can set the allowed UPN suffixes with domain.msc or you can just go straight to the source and stick it into the uPNSuffixs attribute of CN=Partitions,CN=Configuration,[ROOT DOMAIN DN]
Like so
Or better
G:\>adfind -partitions -s base upnsuffixes
AdFind V01.37.00cpp Joe Richards (joe@joeware.net) June 2007
Using server: r2dc1.test.loc:389
Directory: Windows Server 2003
Base DN: cn=partitions,CN=Configuration,DC=test,DC=loc
dn:cn=partitions,CN=Configuration,DC=test,DC=loc
>uPNSuffixes: tracysbarandgrill.com
1 Objects returned
So how do you use this format bind DN in AdFind???
adfind -default -f name=joe -u joe@test.loc -up SomePassword123!
Note: While Active Directory enforces you to use an email style (RFC 822) format string for the UPN, ADAM (Active Directory Application Mode) does not enforce the same standard. You can use single part strings just fine there such as just joe or joeuser or joe.user.
Search Base Formats
Now it is time to discuss the various “DN” formats that can be used for your search base in Active Directory. As you probably know an LDAP query requires you to tell it where in the directory tree to start the search, that is the search base. Most people think you can only specify a DN for this. Normally that may be true but Microsoft was kind enough to give some shortcuts and anyone familiar with AdFind know that I gave more shortcuts but my shortcuts are not the same as the MSFT shortcuts…
Format 1:
The first format for the Base DN is, well, not to surprise you too much, but an actual real live DN. This takes the form of any old DN like… to reuse an example… CN=joe,OU=Users,OU=My,DC=test,DC=loc. But since this is about search bases it could be an OU such as OU=Users,OU=My,DC=test,DC=loc.
AdFind Examples:
adfind -b ou=users,ou=my,dc=test,dc=loc -f name=joe
adfind -b cn=joe,ou=users,ou=my,dc=test,dc=loc -s base
Format 2:
The next format is the GUID of the object. This is a nice format to use if you are tracking an object and want to be able to go to it wherever it might be moved to within the forest. You specify the base in a special format – <GUID=9e0645e9c606d14295ac153d5076d897>.
AdFind Examples
adfind -b “<GUID=ba1ee8b7248b34408c34841740211a81>” -f name=joe
adfind -b “<GUID=9e0645e9c606d14295ac153d5076d897>” -s base
Those two queries correspond to the queries in the Format 1 examples above.
Note: I had to put quotes around the “DN” because if the great than and less than symbols. Those mean something in the command interpreter and I need them to be passed into AdFind unharmed (see http://blog.joeware.net/2008/03/27/1109/).
Format 3
The next format is the SID of the object. This is similar to the GUID format but using SIDs.
AdFind Examples
this space intentionally not an adfind command
adfind -b “<SID=010500000000000515000000aa867905c1c5484bba6236d557040000>” -s base
alternately with any version of Active Directory beyond Windows 2000 you can use
this space intentionally not an adfind command
adfind -b “<SID=S-1-5-21-91850410-1263060417-3577111226-1111>” -s base
As you can see, I don’t have a base DN format with the SID specified that I can use for the OU… why you ask? OU’s aren’t security principals and don’t have SIDs (yes I know this pissed you Novell people off – I get it. heh). So no SID, no way to address the OU by SID. As you can also see there are two different SID formats. I won’t go much into this other than yes there are two formats you can use. Most people, if they do this at all, will likely use the second friendly format and not the HEX format.
SideBar
There is a little sidebar we can take here now related to these Base DN formats. Microsoft was very kind to allow us to output DNs in such a way that these formats are exposed to us… This is called the extended DN format. It is enabled by turning on the proper LDAP control in the LDAP request, for information see http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/aa366980(VS.85).aspx or search for LDAP_SERVER_EXTENDED_DN_OID when MSDN breaks that link for me… 😉
So what does that look like you ask?
AdFind Examples
G:\>adfind -default -f name=joe -dn -extname
AdFind V01.37.00cpp Joe Richards (joe@joeware.net) June 2007
Using server: TEST-DC1.test.loc:389
Directory: Windows Server 2003
Base DN: DC=test,DC=loc
dn:<GUID=9e0645e9c606d14295ac153d5076d897>;<SID=010500000000000515000000aa867905c1c5484bba6236d557040000>;CN=joe,OU=Users,OU=My,DC=test,DC=loc
1 Objects returned
And cooler, as you can see, ANY DN format attributes (not to be confused with string attributes that hold DNs) will get output this way…
G:\>adfind -default -f name=joe memberof directreports managedobjects -extname
AdFind V01.37.00cpp Joe Richards (joe@joeware.net) June 2007
Using server: TEST-DC1.test.loc:389
Directory: Windows Server 2003
Base DN: DC=test,DC=loc
dn:<GUID=9e0645e9c606d14295ac153d5076d897>;<SID=010500000000000515000000aa867905c1c5484bba6236d557040000>;CN=joe,OU=Users,OU=My,DC=test,DC=loc
>memberOf: <GUID=f8fcc524dba94047ac67e36d72195747>;<SID=010500000000000515000000aa867905c1c5484bba6236d578060000>;CN=joegroup,OU=joeperm,OU=TestOU,DC=test,DC=loc
>directReports: <GUID=7806a7be8d6d094b9f9750143cc5151a>;<SID=010500000000000515000000aa867905c1c5484bba6236d5f4010000>;CN=Administrator,CN=Users,DC=test,DC=loc
>managedObjects: <GUID=6186a268b84c374c8563baf56e387d3f>;<SID=010500000000000515000000aa867905c1c5484bba6236d505020000>;CN=Cert Publishers,CN=Users,DC=test,DC=loc
1 Objects returned
And here is an example of the same output for an OU, note the lack of the SID field
G:\>adfind -default -f ou=users -dn -extname
AdFind V01.37.00cpp Joe Richards (joe@joeware.net) June 2007
Using server: TEST-DC1.test.loc:389
Directory: Windows Server 2003
Base DN: DC=test,DC=loc
dn:<GUID=ba1ee8b7248b34408c34841740211a81>;OU=Users,OU=My,DC=test,DC=loc
dn:<GUID=d64d7146973a5a4b928403fba911fb63>;OU=Users,OU=TestOU,DC=test,DC=loc
2 Objects returned